Shrimp farming in Asia is confronted with significant challenges due to disease outbreaks, particularly white faeces syndrome (WFS)

Shrimp farming faces significant challenges due to frequent disease outbreaks that undermine profitability. One particularly severe shrimp disease is white faeces syndrome (WFS), a gastrointestinal disorder commonly reported in Asia. WFS is characterised by a white discolouration in the shrimp gut and the appearance of floating white faecal strings in pond water.
Studies indicate that the co-infection of pathogenic Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) and Vibrio spp. is necessary to induce WFS in shrimp (Aranguren Caro et al., 2021). EHP acts as a primary pathogen, intensifying the impact of opportunistic bacteria such as Vibrio spp., resulting in WFS. Shrimp infected by WFS exhibit retarded growth, significant size variation, elevated feed conversion ratios, and, in severe cases, increased mortality. These issues collectively heighten production costs and pose substantial economic risks for shrimp farmers.
Addressing WFS requires improved pond management strategies along with health management strategies via feed. The latter involves using health-promoting additives to maintain shrimp immunocompetence. Sanacore® GM (Adisseo) is a phytobiotic-based additive with broad- spectrum health-promoting effects. It regulates pathogenic bacteria and parasites while enhancing non-specific immune responses to mitigate the severity of infections on multiple levels.
Combating EHP-WFS through an optimal application strategy
This report presents a detailed evaluation of Sanacore® GM’s efficacy on white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, co-challenged with EHP and Vibrio spp. The trial was conducted in collaboration with ShrimpVet Laboratory, Vietnam. The application strategy was based on a continuous preventive dose of the additive, boosted with a corrective dose when disease symptoms arise.
Two experimental groups, control and treatment, were established. The treatment group received a preventive dose (0.3%) of the additive during the pre-challenge phase (14 days), and the preventive dose was boosted with a corrective dose of 0.5% during the disease challenge period of 10 days (Figure 1). The treatment group returned to the preventive dose during the post- challenge period (35 days). During the challenge phase, EHP-infected shrimp were used as inoculant donors and cohabited with the experimental shrimp for 7 days. After cohabitation, inoculum donor shrimp were removed, and the recipient shrimp were subsequently challenged with Vibrio spp. via the per os method.
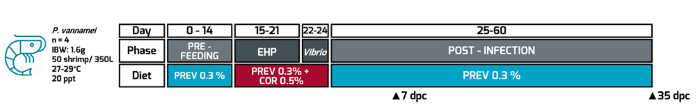
The evaluation of the efficacy of this phytobiotic-based functional additive was carried out at two time points. The first at 7 days post-challenge (dpc) at the early infection stage. The second was at 35 dpc at the end of the infection. During early infection, size variation was monitored as the typical syndrome caused by EHP, resulting from metabolic and immune impairment (Zhang et al., 2023). Mortality was assessed at the end stage, where the combined effects of EHP and Vibrio severely damaged the digestive system, leading to high mortality.
Mitigating the severity of WFS by reducing EHP replication and enhancing shrimp immunity
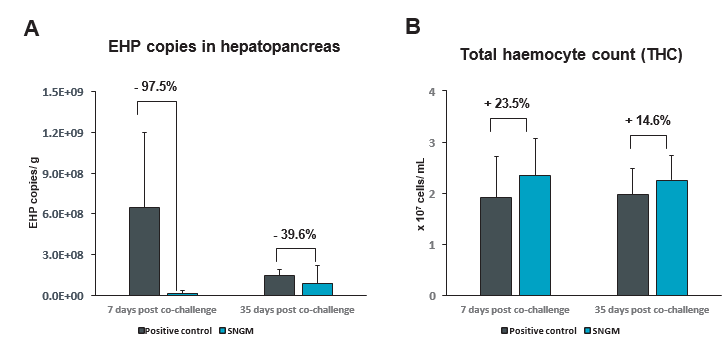
The EHP load in the hepatopancreas is a key indicator of the severity of EHP-WFS infection. Sanacore® GM showed remarkable efficacy in inhibiting EHP replication, reducing its load by 97.5% and 39.6% at the early and late infection stages, respectively(Figure 2A). Such reduction indicates that the additive effectively curbs EHP replication from the outset, thereby attenuating disease progression and offering shrimp protection against EHP.
Haemocytes are central components of the shrimp immune system, involved in pathogen-removal mechanisms such as phagocytosis and encapsulation, as well as in humoral responses such as the release of prophenoloxidase (proPO) or antimicrobial peptides. Recent studies have shown that EHP-WFS infection alters the innate defence immune mechanism, specifically reducing total haemocyte counts (THC), as well as catalase and lysozyme activities (Subash et al., 2022 & 2023).
Enhanced immunocompetence
In the present study, THC levels increased by 23.5% and 14.6% at both early and late stages of infection, respectively, indicating enhanced immunocompetence (Figure 2B). These results suggest the activation of haemocyte proliferation and effective antimicrobial activity against EHP-WFS infection.
Reduced size variation
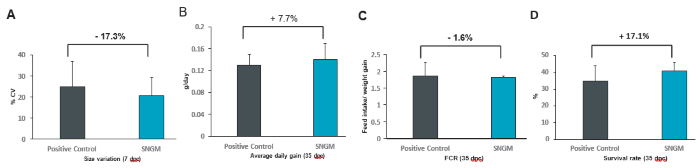
The use of the phytobiotic-based functional additive resulted in benefits in terms of performance parameters. At the early infection stage, supplementation reduced size variation by 17%. Additionally, average daily gain was improved by 8% and FCR by 1.6%. Notably, after 35 days of infection, the survival rate of shrimp in the treatment group increased by 17%. These improvements clearly demonstrate the additive’s efficacy in promoting growth and resistance to EHP-WFS infection.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrated a feed-health management strategy to effectively support shrimp growth and survival in WFS infected shrimp, caused by the co-infection of EHP and Vibrio spp. The preventive supplementation of this phytobiotic-based functional additive Sanacore® GM supports non-specific immunity and provides broad spectrum activity, which are crucial during the early and more susceptible stages of the grow-out period. When disease pressure increases and symptoms appear, boosting feed with a corrective dose of the additive mitigates pathogens proliferation. Sanacore® GM provides feed mills and shrimp farmers with a tool to reduce the impact of disease outbreaks and improve farm profitability by reducing losses associated with WFS.
References
Aranguren Caro, L. F., Mai, H. N., Cruz-Florez, R., Marcos,
F. L. A., Alenton, R. R. R., & Dhar, A. K. (2021). Experimental reproduction of White Feces Syndrome in whiteleg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. PloS one, 16(12), e0261289. https://doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261289
Chen, I., Mamora M., Isern-Subich, M. M., & Nuez-Ortín W.
G. (2023). Efficacy of a phytobiotic-based additive to reduce the severity of EHP-WFS outbreaks in field conditions. AQUA Culture Asia Pacific, May/June, P31- 33. bit.ly/3BO1ZDc Subash, P., Chrisolite, B., Sivasankar, P., George, M. R., Amirtharaj, K. V., Padmavathy, P., … & Mageshkumar, P. (2023). White feces syndrome in Penaeus vannamei is potentially an Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) associated pathobiome origin of Vibrio spp. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 198, 107932. DOI: 10.1016/j.jip.2023.107932
Subash, P., Uma, A., & Ahilan, B. (2022). Early responses in Penaeus vannamei during experimental infection with Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP) spores by injection and oral routes. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 190, 107740. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2022.107740
Zhang, L., Zhang, S., Qiao, Y., Cao, X., Cheng, J., Meng, Q., & Shen, H. (2023). Dynamic Interplay of Metabolic and Transcriptional Responses in Shrimp during Early and Late Infection Stages of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316738

I-Tung Chen, PhD, is Project Research Manager Aquaculture Health, Adisseo.
Email: i-tung.chen@adisseo.com
Maria Mercè Isern-Subich, DVM, is Global Product Manager Health Aquaculture, Adisseo.
Waldo G. Nuez-Ortín, DVM, PhD, is Global R&D Manager Aquaculture, Adisseo.
Khin Thiri Khit, R&D Specialist, ShrimpVet Laboratory, Vietnam
Phuc Hoang, Managing Director, ShrimpVet Laboratory, Vietnam
Loc Tran, Founder & Director, ShrimpVet Laboratory, Vietnam




